Check out our new “About MXenes” handout [PDF] and learn all about MXenes.

Scanning electron microscope image of multilayered Ti3C2 MXene. B. Anasori, et al. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2,
16098.
MXenes are a family of
two-dimensional (2D) inorganic compounds with the general formula of Mn+1XnTx,
where M is an early transition metal, X is carbon and/or nitrogen, and T is a
functional group on the surface of a MXene (typically O, OH and F) (M. Naguib,
et al. Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 992). MXenes have the high metallic
conductivity of transition metal carbides, and are (unlike other 2D materials
like graphene) hydrophilic because of their hydroxyl- and oxygen-terminated
surfaces. MXenes were first discovered in 2011 at Drexel University, as a
result of selectively etching the A layer out of bulk ternary transition metal
carbides and nitrides, known as MAX phases, which yields multilayered MXenes.
To increase surface area and accessibility of its surface, multilayered MXenes
typically undergo further processing to yield solutions of delaminated MXenes.
Due to their hydrophilicity, MXenes
can be processed in aqueous and polar organic solvents to form stable colloidal
solutions that can be filtered to form freestanding films and spray-coated to
form transparent conductive coatings. This provides a greater of potential
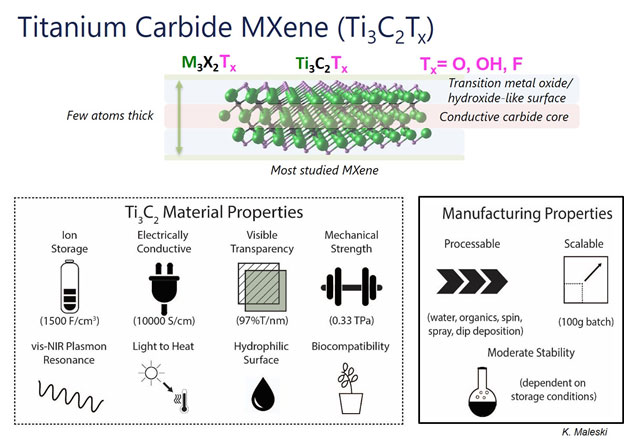
applications for this family of materials. The first MXene discovered was Ti3C2 and it was initially investigated for its electrochemical properties in
batteries and supercapacitors (B. Anasori, et al. Nature Reviews Materials,
2017, 2, 16098). In the past several years, however, over two dozen
MXenes have been discovered along with dozens of other applications.
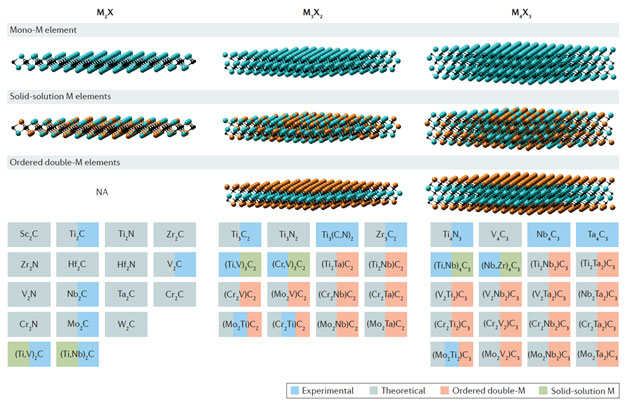
Experimentally synthesized and theoretically predicted MXenes. B. Anasori, et al. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2,
16098.
MXene applications that have been
explored beyond energy storage include sprayable electromagnetic interference
shielding, which it was found to be the best performing synthetic material for
this application per thickness of material (F. Shahzad, et al. Science, 2016, 353 (6304): 1137). Other applications that have been found are sprayable
antennas (A. Sarycheva, et al. Science Advances, 2018, 4(9), eaau0920.),
several biomedical applications (K. Huang, et al. Chemical Society Reviews,
2018, 14, 5109), water purification (K. Rasool, et al. Materials
Today, 2019. "Water treatment and environmental remediation
applications of two-dimensional metal carbides (MXenes).") and beyond.
Nitride MXenes, which are synthesized by different procedures than carbide
MXenes, offer other potential applications due to their high electrical
conductivity values and plasmonic properties (P. Urbankowski, et al. Nanoscale,
2017, 9(45), 17722). The world of MXene synthesis and application
development is growing at a rapid rate. This family of materials has outperformed
materials used in many applications and has the potential to transform the
incorporation of nanotechnology in everyday life.

Additional Reading:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MXenes
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/adma.201304138
- https://www.nature.com/articles/natrevmats201698?draft=journal
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/cs/2018/c7cs00838d#!divAbstract
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1359028618301426
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/adma.201804779