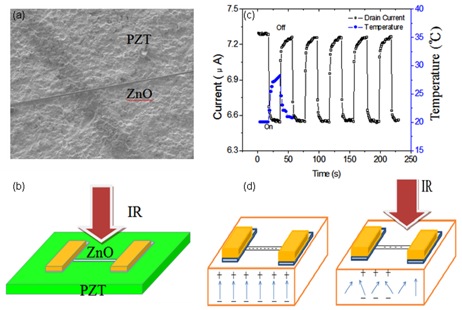
 ZnO-PZT field effect transistor. (a) SEM image showing a single ZnO NW bridging two patches of PZT. (b) A schematic illustration of device configuration under IR illumination. (c) The drain current as a function of time modulated by IR laser of 250 mW with a light on or off PZT with upward polarization. The temperature rise correlates with the current drop. (d) IR illumination on the PZT with upward polarization decreases the positive bound charge density at the top surface of the PZT, which decreases the electron carrier concentration in the ZnO NW and decreases the drain current.
ZnO-PZT field effect transistor. (a) SEM image showing a single ZnO NW bridging two patches of PZT. (b) A schematic illustration of device configuration under IR illumination. (c) The drain current as a function of time modulated by IR laser of 250 mW with a light on or off PZT with upward polarization. The temperature rise correlates with the current drop. (d) IR illumination on the PZT with upward polarization decreases the positive bound charge density at the top surface of the PZT, which decreases the electron carrier concentration in the ZnO NW and decreases the drain current.Research on new transistors that have potential remote or wireless applications by Professor Wei-Heng Shih and his collaborators has recently appeared in the journal Nanotechnology (impact factor 3.979).
"Single ZnO nanowire–PZT optothermal field effect transistors" by Chun-Yi Hsieh, Meng-Lin Lu, Ju-Ying Chen, Yung-Ting Chen, Ph.D. students in the Department of Physics at National Taiwan University (TWU); Professor Yang-Fang Chen of TWU; affiliated faculty member Professor Wan Y. Shih; and Professor Wei-Heng Shih reports that due to the change of polarization of the piezoelectric substrate under laser light, the current sensitivity of the novel optothermal field effect transistor is about three orders of magnitude higher than that of the typical photogating transistors based on carbon nanotube on SiO2/Si substrate.
News on the findings of this publication appeared on nanotechweb.org.