September 26, 2016
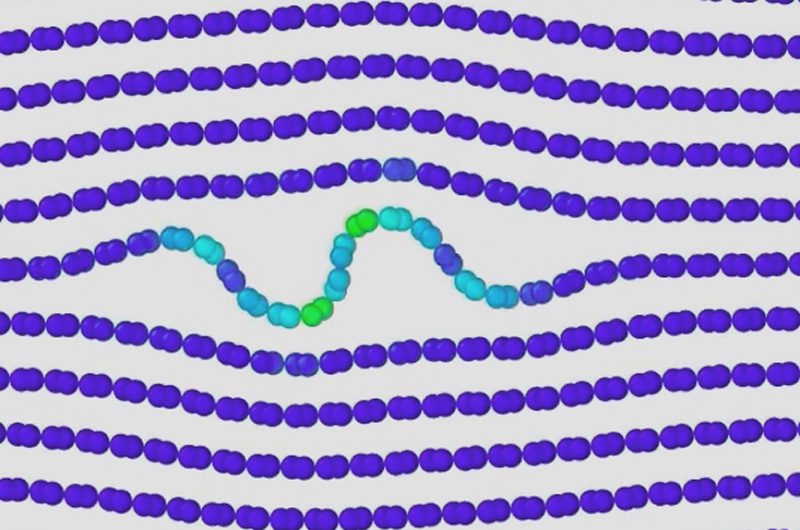
Every material can bend and break. Through nearly a century’s worth of research, scientists have had a pretty good understanding of how and why. But, according to new findings from Drexel University materials science and engineering researchers, our understanding of how layered materials succumb to stresses and strains was lacking. The report suggests that, when compressed, layered materials — everything from sedimentary rocks, to beyond-whisker-thin graphite — will form a series of internal buckles, or ripples, as they deform.
Read More
-
September 23, 2016
Dr. Kalra Featured in NBC News' Article on the Galaxy Note 7.
Read More
-
September 23, 2016
A paper by Daniel Lawrence and Prof. Vibha Kalra (with collaborators from Los Alamos National Lab) entitled “High-energy density nanofiber-based solid-state supercapacitors“ has been featured as a HOT article.
Read More
-
September 22, 2016
Throughout the Fall 2016 quarter, several Drexel ECE PhD students will be conducting seminars focusing on their cutting-edge research within computer engineering.
Read More
-
September 22, 2016
Drexel University faculty, ECE faculty, ECE students, and visiting scholars will be presenting lectures every Tuesday throughout the Fall 2016 quarter.
Read More
-
September 21, 2016
Dr. Masoud Soroush has been selected for recognition by I&EC Research in their inaugural Excellence in Review Awards for 2016.
Read More
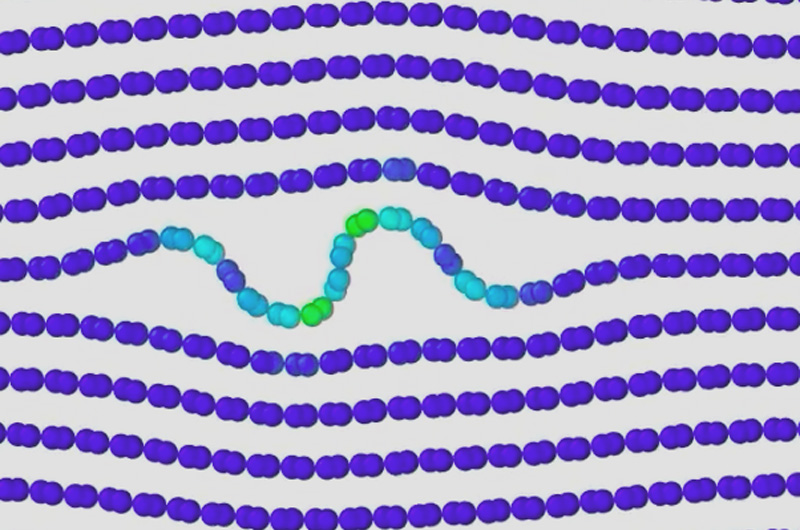
September 20, 2016
New findings from Drexel Materials researchers suggest that, when compressed, layered materials will form a series of internal buckles, or ripples, as they deform, vastly expanding our understanding of how layered materials succumb to stresses and strains.
Read More
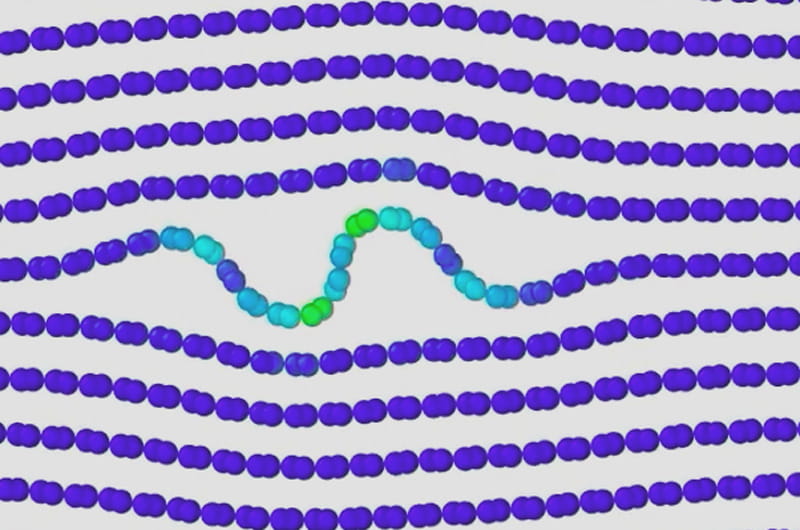
September 19, 2016
Every material can bend and break. Through nearly a century’s worth of research, scientists have had a pretty good understanding of how and why. But, according to new findings from Drexel University materials science and engineering researchers, our understanding of how layered materials succumb to stresses and strains was lacking. The report suggests that, when compressed, layered materials — everything from sedimentary rocks, to beyond-whisker-thin graphite — will form a series of internal buckles, or ripples, as they deform.
Read More
-
September 19, 2016
Read More
-
September 16, 2016
Read More
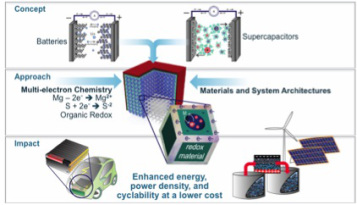
September 12, 2016
In a recent edition of Nature Communications, Drexel Materials researchers offer a unified route for bringing our energy storage and distribution capabilities level with our energy production and consumption.
Read More

September 09, 2016
The College of Engineering was among ten universities nationwide to be honored by the American Society of Engineering Education (ASEE) with an award for excellence in educating our nation’s veterans.
Read More

September 09, 2016
Dr. Robert M. Koerner, ’56, was recently honored at the 2016 Geo-Chicago Conference organized by the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) Geo-environmental Engineering Committee of the GEO-Institute. Highlighted were Dr. Koerner’s considerable contributions to the field of civil engineering along with his outstanding leadership within the geo-profession and the civil engineering community at large.
Read More
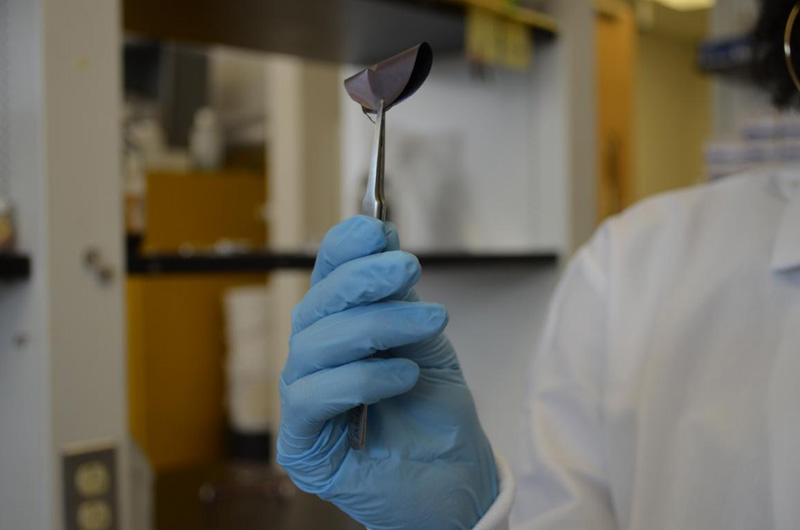

September 08, 2016
MXene, a nanomaterial discovered by Drexel Materials scientists, could be the key to shielding electronic devices from electromagnetic interference, like a television buzzing when a cell phone is near.
Read More

September 08, 2016
Since June, the Drexel Hyperloop team has made great strides to prove the feasibility of their pod design. At the end of last academic year, the team lost over 80 members to graduation, leaving 15 members to regroup and recruit. And they were successful, with over 60 members joining over the summer, most of whom are sophomores and pre-juniors. These students have proven themselves above and beyond over the last 2 months with a strong commitment to maintaining a higher level of efficiency and production than was expected.
Read More
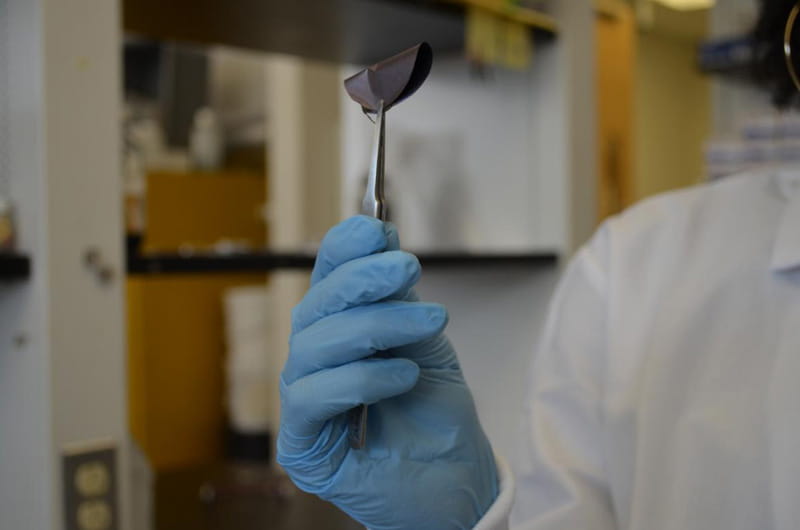

September 08, 2016
If you’ve ever heard your engine rev through your radio while listening to an AM station in your car, or had your television make a buzzing sound when your cell phone is near it, then you’ve experienced electromagnetic interference. This phenomenon, caused by radio waves, can originate from anything that creates, carries or uses an electric current, including television and internet cables, and, of course cell phones and computers. A group of researchers at Drexel University and the Korea Institute of Science & Technology is working on cleaning up this electromagnetic pollution by containing the emissions with a thin coating of a nanomaterial called MXene.
Read More
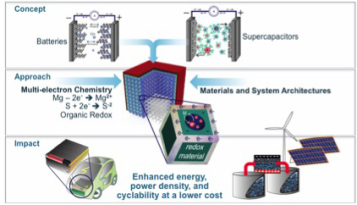
September 07, 2016
Energy storage is a limiting factor that researchers have been aware of for quite a while, but their work to improve our storage devices has taken many, disparate directions. In a recent edition of Nature Communications, Drexel materials science and engineering researchers Yury Gogotsi, PhD, and Maria Lukatskaya, PhD, who have been surveying the landscape of energy storage research for years, offer a unified route for bringing our energy storage and distribution capabilities level with our energy production and consumption.
Read More

September 06, 2016
A new student chapter of the American Society for Engineering Education (ASEE) will have its first general body meeting at the beginning of the fall quarter.
Read More
-
September 04, 2016
Read More